Digestive Health
thumbnail
Specialty Nutrients
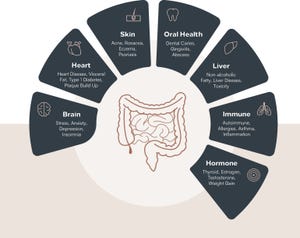
How to formulate the new biotic productsHacking innovative probiotic prebiotic postbiotic products
Biotics provide unique health benefits that can differentiate your brand and attract a broader range of health-focused consumers.
Subscribe and receive the latest insights on the health and nutrition industry.
Join 37,000+ members. Yes, it's completely free.











































.png?width=800&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)